Web Development
Context API Vs Redux: Which Is Better And When To Use Them?
Last Updated: 21st July, 2023State Management in React: Learn about managing state in React with Redux vs Context API. Discover their features and use cases to make an informed decision.


Redux vs Context API
Did you know that managing state in a large-scale React application can be a challenging task? Imagine a scenario where you have a complex web application with numerous components that need to share and synchronize data. In such cases, efficient state management becomes crucial for maintaining a well-structured and responsive user interface. This article delves into the world of state management in React, focusing on two popular solutions: Redux and Context API. We'll explore their features, benefits, and use cases to help you make an informed decision when it comes to choosing the right state management approach for your project, and specifically compare Redux vs Context API.
What is State Management in React?
State management refers to the process of storing and managing the data that drives the behaviour and appearance of an application. In simpler terms, it's like having a central repository that holds all the important information for your application to work correctly. Just as a conductor orchestrates the musicians in an orchestra, state management allows different parts of your application to communicate and synchronize with each other seamlessly. React state management is a way of controlling the data that React components need to present themselves. This data is usually stored in the state object of the component. If the state object changes, the object will re-render itself.
Redux

Redux
Redux is a predictable state container library for JavaScript applications, commonly used with React and other frameworks. It provides a centralized repository for managing application state, and makes it easy to view and update state between components.
Key concepts in Redux:
- Store: A container is a JavaScript object that holds the entire application state. Application data has only one source of truth. In Redux, the state is immutable, which means it cannot be changed directly. Instead, referral actions create change.
- Actions: Actions are simple JavaScript objects that represent intentions to change state. They explain what happened in the application. Actions must have a type property that specifies the type of action they are performing. Additional data can be added to the action payload property to provide additional information.
- Reducers: Reducers are pure functions that are responsible for executing actions and updating the state of the application. The reducer takes the current state and action as input and returns a new state. Reducers should not modify an existing state but should create a new state object.
- Dispatch: Dispatch is a function provided by Redux that sends an action to the repository. It is used to instigate state change. When an event is returned, Redux sends it to reducers, which then update the state based on the event type.
- Middleware: Middleware is a way to extend Redux actions. It stays between sending the action and receiving the reduction. The middle processor can cancel actions, perform other tasks, and modify actions before the reducer is reached. Middleware examples include logging, asynchronous actions, and API calls.
- Connect: Connect is a superior feature provided by the React Redux library. It connects React components to a Redux container, allowing components to access the container environment and pass actions.
Basic Redux Flow:
- Define actions: Create an action type as a constant and create an action constructor function that returns an action object. An event scheduler overlays the event schedule with the appropriate production load.
- Create reducers: Write pure functions (reducers) that perform operations and update the state accordingly. Reducers specify how to modify the state based on the nature of the event.
- Create a store: Create a Redux store using the createStore function provided by Redux. Set up the root reducer that combines multiple reducers into one. Additionally, you can apply middleware using the applyMiddleware function.
- Connect components: Use the connect function from React Redux to connect components to the store. This enables components to access the state and dispatch actions.
- Dispatch actions: Dispatch actions using the provided shipping services of the warehouse. The actions flow through the middleware (if present) and then reach the reducers, which update the state based on the action type.
- Access state: Components associated with the store can access the state through props. If the state changes, the associated components will re-render themselves.
- Modify state: Components send actions to modify the state. The reducers will process the actions and update the state accordingly.
Context API
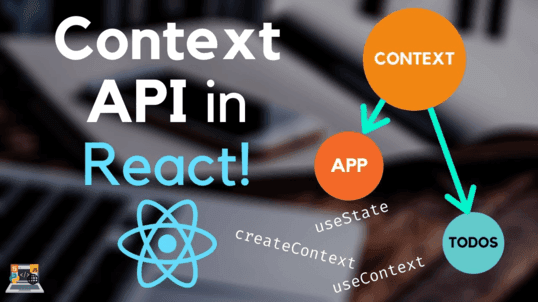
Context API
The Context API is a feature introduced in React that allows data to be shared between components without passing props through between components. It provides a method for creating a global context to which any object in the object tree can access.
Key concepts in Context API:
- Context: A Context is created using the createContext function provided by React. It returns an object that has two properties: Provider and Consumer.
- Provider: The provider component is used to bind to the part of the component tree where you want to provide a reference. It accepts a value prop, which represents the data or state you want to share. The provider component ensures that all child components can access the shared data.
- Consumer: The consumer component is used to access the data shared in the component. It uses a render prop pattern or other React hooks to consume the reference value. The consumer component automatically records changes to the reference value and updates the component when the value changes.
Basic usage of Context API:
- Create a Context: Use the `createContext` function to create a new context.
For example:
| const MyContext = React.createContext(); |
|---|
- Wrap Components with Provider: Wrap the desired portion of the component tree with the `provider` component. Pass the shared data as the `value` prop.
For example:
| <MyContext.Provider value={shareData}>
{/* Components within the Provider can access the sharedData */}
<Component1 />
<Component2 />
| </MyContext.Provider> |
|---|
- Consume Context in Components:
- Class Components: Use the `Consumer` component with a render prop to consume the context value. For example:
| <MyContext.Consumer>
{value => (
<div>{value}</div>
)}
| </MyContext.Consumer> |
|---|
- Functional Components(Using React Hooks): Use the `useContext` hook to access the context value. For example:
| const value = useContext(MyContext); |
|---|
Choosing the Right Approach: React Context API vs Redux
When deciding between Redux and the Context API, consider the complexity and scale of your application. Redux shines in large applications where you have a massive amount of shared state or need advanced features like time-travel debugging. It excels in scenarios where predictable and explicit control over state changes is essential.
On the other hand, if you're working on a smaller project or your state management needs are relatively straightforward, the Context API can be a suitable choice. It provides a more lightweight and convenient solution without the need for additional dependencies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, when deciding when to use the Context API vs Redux for state management in React, it is important to consider the complexity and scale of your application. Redux is recommended for large-scale projects with extensive shared state and advanced debugging needs, offering explicit control and time-travel capabilities. On the other hand, the Context API is a lightweight option suitable for smaller projects or simpler state management requirements, providing convenience and eliminating prop drilling. Evaluate your project's specific needs to determine whether to utilize the Context API or Redux for effective state management in React.
Read our recent blog on "Unlocking Secrets: Best Practices for Responsive Web Design".
Want to learn more about Web Development from scratch? Join AlmaBetter and develop a deep understanding of Web Development trends.
Frequently asked Questions
Q1: What is state management in React, and why is it important?
Q2: What is Redux, and how does it differ from the Context API?
Q3: When should I choose Redux over the Context API?
Q4: When should I choose the Context API over Redux?
Related Articles
Top Tutorials
- Courses
- Advanced Certification in Data Analytics & Gen AI Engineering
- Advanced Certification in Web Development & Gen AI Engineering
- MS in Computer Science: Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence
- MS in Computer Science: Cloud Computing with AI System Design
- Professional Fellowship in Data Science and Agentic AI Engineering
- Professional Fellowship in Software Engineering with AI and DevOps
- Join AlmaBetter
- Sign Up
- Become A Coach
- Coach Login
- Policies
- Privacy Statement
- Terms of Use
- Contact Us
- admissions@almabetter.com
- 08046008400
- Official Address
- 4th floor, 133/2, Janardhan Towers, Residency Road, Bengaluru, Karnataka, 560025
- Communication Address
- Follow Us
© 2025 AlmaBetter
